So, I thought I'd be easier if instead of organizing this in weeks I do it in months.
Charades (with movies).
On this class we played charades but with movies, the idea was that we had to make two teams and one team had to choose a movie, tell the name to a member of the other team, the he had to act it and his team had to find out which movie was he acting.
Science Fair design.
We were asked to make a design for the science fair and I came up with this idea, I call it "We are the universe"
This one is different than the one I made in class but it's the same idea, that there's another world and we're leaving this one because we can't live here anymore.
We also solved a crime which was called "A quiet morning at the office".
We had the science oral presentations, and my topic was solid waste:
Solid waste:
Saturday, October 23, 2010
Friday, September 24, 2010
Seventh Week (September 20th to September 24th).
This week we had the science oral presentations and my topic was "Intertidal Zones".
Intertidal Zones
 Intertidal or littoral zones make up the coasts around the world; this biome is located where the sandy beaches meet the sea between the high and low tide zones, these rocky shores are exposed and submerged by the tides at least twice a day, depending on where the coast is affects the temperature of air and water in the biome. Coast lines that are in the tropics are warmer, whereas arctic coast have cold water and air, the shape of the coast affects the intensity of the waves, the straight lined coasts are hit more intensely by the water, but rounded coasts, made of bays are usually calmer and the water isn´t as rough at high tide.
Intertidal or littoral zones make up the coasts around the world; this biome is located where the sandy beaches meet the sea between the high and low tide zones, these rocky shores are exposed and submerged by the tides at least twice a day, depending on where the coast is affects the temperature of air and water in the biome. Coast lines that are in the tropics are warmer, whereas arctic coast have cold water and air, the shape of the coast affects the intensity of the waves, the straight lined coasts are hit more intensely by the water, but rounded coasts, made of bays are usually calmer and the water isn´t as rough at high tide.
Intertidal Zones
Intertidal zones.
 Intertidal or littoral zones make up the coasts around the world; this biome is located where the sandy beaches meet the sea between the high and low tide zones, these rocky shores are exposed and submerged by the tides at least twice a day, depending on where the coast is affects the temperature of air and water in the biome. Coast lines that are in the tropics are warmer, whereas arctic coast have cold water and air, the shape of the coast affects the intensity of the waves, the straight lined coasts are hit more intensely by the water, but rounded coasts, made of bays are usually calmer and the water isn´t as rough at high tide.
Intertidal or littoral zones make up the coasts around the world; this biome is located where the sandy beaches meet the sea between the high and low tide zones, these rocky shores are exposed and submerged by the tides at least twice a day, depending on where the coast is affects the temperature of air and water in the biome. Coast lines that are in the tropics are warmer, whereas arctic coast have cold water and air, the shape of the coast affects the intensity of the waves, the straight lined coasts are hit more intensely by the water, but rounded coasts, made of bays are usually calmer and the water isn´t as rough at high tide.The intertidal zones can be broken out into 4 zones:
The upper littoral zone also called the splash zone is only flooded during high tide and its exposed to the sun for the rest, hardly any vegetation grows here.
The upper-mid littoral zone is equally submerged and exposed for making temperatures less extreme, however wave action is more extreme and more vegetation such as seaweed grows here.
The lower-mid littoral zone is where most vegetation grows, there’s more energy in here and the water coverage allows for sufficient light for plant growing.
The lower littoral zone however is where larger organisms start to appear that can only leave in water and feed on the secondary consumers.
The intertidal region is an important model system for the study of ecology. The region contains a high diversity of species, and the different zones ranges are compressed into very narrow bands. This makes it simple to study species across their entire cross-shore range, something that can be extremely difficult
Sixth Week (September 13th to September 14th).
This week was short because we had a break due to the independence celebrations:
-Jeff Dunham Jokes:
We listened to Jeff Dunham's jokes and it was a lot of fun:
(Pretty self explanatory).
-Jeff Dunham Jokes:
We listened to Jeff Dunham's jokes and it was a lot of fun:
(Pretty self explanatory).
Fifth Week (September 6th to September 10th).
This week we also answered the book on a very creative and innovative way:
-The Activity.
In this activity the rules were that the teacher said the exercise we had to solve, and when said GO! We had to run as fast as we could to the blackboard and solve it as fast as possible, and whoever finished first won
-The Activity.
In this activity the rules were that the teacher said the exercise we had to solve, and when said GO! We had to run as fast as we could to the blackboard and solve it as fast as possible, and whoever finished first won
Fourth Week (August 30th to September 4th).
This week we got our books and for answering them we played "Charades".
-Charades:
 We all have played charades, the basic idea is to get a word, verb, action, etc. and act it out, then the audience should find out what are you trying to say and whoever says it first wins.
We all have played charades, the basic idea is to get a word, verb, action, etc. and act it out, then the audience should find out what are you trying to say and whoever says it first wins.
The activity was a lot of fun, and a very creative way of taking the conventionality of answering a book sitting on your desk and making it a lot of fun.
We also made a happy place project:
-Happy Fun Place:
Rooms:
1. Resting room.
2. Movies room. (Cinema)
3. Playing room.
4. Intimacy room.
5. Bar.
6. Spa.
Areas:
1. Swimming pool.
2. Restaurant.
3. Football field.
4. Tennis field.
5. Basketball field.
6. Volleyball field.
Music:
1. There is a jukebox with over a million song and artists for you to choose from.
2. There are iPods with headphones on the walls for you to listen to.
Food and drinks:
1. Pastas.
2. Fast foods.
3. Sodas.
4. Alcohol (Only over 18).
Furniture:
1. Big beds.
2. Couches.
3. Chairs.
4. Tables.
This week was a lot of fun, my goals for next week is being more responsible with the book.
-Charades:
 We all have played charades, the basic idea is to get a word, verb, action, etc. and act it out, then the audience should find out what are you trying to say and whoever says it first wins.
We all have played charades, the basic idea is to get a word, verb, action, etc. and act it out, then the audience should find out what are you trying to say and whoever says it first wins.The activity was a lot of fun, and a very creative way of taking the conventionality of answering a book sitting on your desk and making it a lot of fun.
We also made a happy place project:
-Happy Fun Place:
Rooms:
1. Resting room.
2. Movies room. (Cinema)
3. Playing room.
4. Intimacy room.
5. Bar.
6. Spa.
Areas:
1. Swimming pool.
2. Restaurant.
3. Football field.
4. Tennis field.
5. Basketball field.
6. Volleyball field.
Music:
1. There is a jukebox with over a million song and artists for you to choose from.
2. There are iPods with headphones on the walls for you to listen to.
Food and drinks:
1. Pastas.
2. Fast foods.
3. Sodas.
4. Alcohol (Only over 18).
Furniture:
1. Big beds.
2. Couches.
3. Chairs.
4. Tables.
This week was a lot of fun, my goals for next week is being more responsible with the book.
Friday, August 27, 2010
Third Week (August 23rd to August 27th).
This week we made a role play and presentations of biomes:
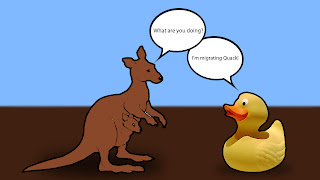
The Kangaroo, the Duck, and the Iguana:
Kangaroo: Hey duck!
Duck: Hey!
Kangaroo: What are you doing?
Duck: I'm migrating, Quack! To Alaska, Quack!
Kangaroo: Oh my god! can I go, please?
Duck: Yeah I guess so.
Iguana: But kangaroo, you can´t go there, you'll die, its not your habitat!
Kangaroo: I don´t care! I'll go to Alaska even if it's the last thing I do.
Lest go Duck!
Duck: Alright, get on my wings!
They got to Alaska...
Duck: We made it kangaroo, we made it!
Kangaroo: Yeah...
Kangaroo died...
THE END.
Geography
Deserts are part of a wide classification of regions that, on an average annual basis, have a moisture deficit. Deserts are located where vegetation cover is sparse to almost nonexistent. Deserts take up about one third of the Earth's land surface. Hot deserts usually have a large diurnal and seasonal temperature range, with high daytime temperatures, and low nighttime temperatures. In hot deserts the temperature in the daytime can reach 45 °C or higher in the summer, and dip to 0 °C or lower in the winter. Water acts to trap infrared radiation from both the sun and the ground, and dry desert air is incapable of blocking sunlight during the day or trapping heat during the night. Thus, during daylight most of the sun's heat reaches the ground, and as soon as the sun sets the desert cools quickly by radiating its heat into space. Urban areas in deserts lack large daily temperature variations.
aRcTIC TUNDRA
The Arctic tundra is a vast area of stark landscape and is frozen for much of the year. The soil there is frozen from 25–90 cm down, and it is impossible for trees to grow. Instead, bare and sometimes rocky land can only support low growing plants such as moss, and lichen. There are two main seasons, winter and summer, in the polar tundra areas. During the winter it is very cold and dark, with the average temperature around −28 °C, sometimes dipping as low as −50 °C. However, extreme cold temperatures on the tundra do not drop as low as those experienced in taiga areas further south. During the summer, temperatures rise somewhat, and the top layer of the permafrost melts, leaving the ground very soggy. The tundra is covered in marshes, lakes, bogs and streams during the warm months.
antaRcTIC TUNDRA
alpine TUNDRA

The Kangaroo, the Duck, and the Iguana:
Kangaroo: Hey duck!
Duck: Hey!
Kangaroo: What are you doing?
Duck: I'm migrating, Quack! To Alaska, Quack!
Kangaroo: Oh my god! can I go, please?
Duck: Yeah I guess so.
Iguana: But kangaroo, you can´t go there, you'll die, its not your habitat!
Kangaroo: I don´t care! I'll go to Alaska even if it's the last thing I do.
Lest go Duck!
Duck: Alright, get on my wings!
They got to Alaska...
Duck: We made it kangaroo, we made it!
Kangaroo: Yeah...
Kangaroo died...
THE END.
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Deserts are defined as areas with an average annual precipitation of less than 250 millimeters per year, or as areas where more water is lost by evapotranspiration than falls as precipitation. In the Köppen climate classification system, deserts are classed as BWh (hot desert) or BWk (temperate desert). In the Thornthwaite climate classification system, deserts would be classified as arid mega thermal climates.
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Deserts are defined as areas with an average annual precipitation of less than 250 millimeters per year, or as areas where more water is lost by evapotranspiration than falls as precipitation. In the Köppen climate classification system, deserts are classed as BWh (hot desert) or BWk (temperate desert). In the Thornthwaite climate classification system, deserts would be classified as arid mega thermal climates.
Geography
Deserts are part of a wide classification of regions that, on an average annual basis, have a moisture deficit. Deserts are located where vegetation cover is sparse to almost nonexistent. Deserts take up about one third of the Earth's land surface. Hot deserts usually have a large diurnal and seasonal temperature range, with high daytime temperatures, and low nighttime temperatures. In hot deserts the temperature in the daytime can reach 45 °C or higher in the summer, and dip to 0 °C or lower in the winter. Water acts to trap infrared radiation from both the sun and the ground, and dry desert air is incapable of blocking sunlight during the day or trapping heat during the night. Thus, during daylight most of the sun's heat reaches the ground, and as soon as the sun sets the desert cools quickly by radiating its heat into space. Urban areas in deserts lack large daily temperature variations.
Many deserts are formed by rain shadows; mountains blocking the path of precipitation to the desert. Deserts are often composed of sand and rocky surfaces. Sand dunes called ergs and stony surfaces called Hamada surfaces compose a minority of desert surfaces. Exposures of rocky terrain are typical, and reflect minimal soil development and sparseness of vegetation. The soil is rocky because of the low chemical weathering.
Bottomlands may be salt-covered flats. Eolian processes are major factors in shaping desert landscapes. Polar deserts have similar features, except the main form of precipitation is snow rather than rain. Antarctica is the world's largest cold desert. Some of the barren rock is to be found in the so-called Dry Valleys of Antarctica that almost never get snow, which can have ice-encrusted saline lakes that suggest evaporation far greater than the rare snowfall due to the strong katabatic winds that evaporate even ice.
The largest hot desert is the Sahara in northern Africa, covering 9 million square kilometers and 12 countries.
The 10 largest deserts | |||
Rank | Desert | Area (km²) | Area (mi²) |
1 | 13,829,430 | 5,339,573 | |
2 | 13,700,000+ | 5,300,000+ | |
3 | 9,100,000+ | 3,320,000+ | |
4 | 2,330,000 | 900,000 | |
5 | 1,300,000 | 500,000 | |
6 | 900,000 | 360,000 | |
7 | 670,000 | 260,000 | |
8 | 647,000 | 250,000 | |
9 | 520,000 | 200,000 | |
10 | 492,000 | 190,000 | |
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra. In tundra, the vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, sedges and grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra. The ecotone between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline.
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra. In tundra, the vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, sedges and grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra. The ecotone between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline.
aRcTIC TUNDRA
The Arctic tundra is a vast area of stark landscape and is frozen for much of the year. The soil there is frozen from 25–90 cm down, and it is impossible for trees to grow. Instead, bare and sometimes rocky land can only support low growing plants such as moss, and lichen. There are two main seasons, winter and summer, in the polar tundra areas. During the winter it is very cold and dark, with the average temperature around −28 °C, sometimes dipping as low as −50 °C. However, extreme cold temperatures on the tundra do not drop as low as those experienced in taiga areas further south. During the summer, temperatures rise somewhat, and the top layer of the permafrost melts, leaving the ground very soggy. The tundra is covered in marshes, lakes, bogs and streams during the warm months.
antaRcTIC TUNDRA
 |
| The tundra model I made |
Antarctic tundra occurs on Antarctica and on several Antarctic and subantarctic islands, including South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands and the Kerguelen Islands. Antarctica is mostly too cold and dry to support vegetation, and most of the continent is covered by ice fields. However, some portions of the continent, particularly the Antarctic Peninsula, have areas of rocky soil that support plant life. The flora presently consists of around 300–400 lichens, 100 mosses, 25 liverworts, and around 700 terrestrial and aquatic algae species, which live on the areas of exposed rock and soil around the shore of the continent. Antarctica's two flowering plant species, the Antarctic hair grass (Deschampsia Antarctica) and Antarctic pearlwort (Colobanthus quitensis), are found on the northern and western parts of the Antarctic Peninsula.
In contrast with the Arctic tundra, the Antarctic tundra lacks a large mammal fauna, mostly due to its physical isolation from the other continents
In contrast with the Arctic tundra, the Antarctic tundra lacks a large mammal fauna, mostly due to its physical isolation from the other continents
alpine TUNDRA
 |
| The tundra model I made |
Alpine tundra is an ecozone that does not contain trees because it has high altitude. Alpine tundra is distinguished from arctic tundra, because alpine tundra typically does not have permafrost, and alpine soils are generally better drained than arctic soils. Alpine tundra transitions to subalpine forests below the tree line; stunted forests occurring at the forest-tundra ecotone are known as Krummholz.
Alpine tundra occurs in mountains worldwide. The flora of the alpine tundra is characterized by dwarf shrubs close to the ground. The cold climate of the alpine tundra is caused by the low air pressure, and is similar to polar climate.
I liked this week, because we made a role play and it was a fun process making it, I also learned about biomes and other things. I think I could’ve done better with my presentation.
Alpine tundra occurs in mountains worldwide. The flora of the alpine tundra is characterized by dwarf shrubs close to the ground. The cold climate of the alpine tundra is caused by the low air pressure, and is similar to polar climate.
I liked this week, because we made a role play and it was a fun process making it, I also learned about biomes and other things. I think I could’ve done better with my presentation.
Friday, August 20, 2010
Second Week (August 16th to August 20th).
So this week we worked a bit more but we still did some fun activities:
-What makes people happy?
Different people have different opinions on what makes people happy. Some would say it's getting a raise. Others would say it's having a wonderful and meaningful life. There have even been quite a few who have more specific answers according to their personal life.
-10 things that make people happy:
1.- Being treated right.
2.- Being respected.
3.- Being loved.
4.- Being important.
5.- Doing what they like.
6.- Relaxing.
7.- Having friends.
8.- Being with the people they love.
9.- Having peace.
10.- Having fun.
-10 things that make me happy:
6.- Relaxing.
7.- Having friends.
8.- Being with the people they love.
9.- Having peace.
10.- Having fun.
-10 things that make me happy:
1.- When people respect me.
2.- When I'm treated right.
3.- When I have fun.
4.- When I do things i like.
5.- When I make other people happy.6.- When I'm with my loved ones.
7.- When I'm with my family.
8.- When I see that someone cares about me.
9.- When people make me laugh when I'm sad.
10.-When I'm peaceful with myself.
A Little questionnaire:
1.- What's the most important thing in life? Why?
A: Yourself and being happy, being with the people you love and making them happy.
2.- What's more important family or money? Why?
A: Family, because the money comes and goes but you family is the ones you love and will always be your family.
Ten rules to have a happy life:
Ten rules to have a happy life:
1.- Enjoy your life.
2.- Always smile, always laugh.
3.- Have a positive attitude.
4.- Get along with others.
5.- Always do your best.
6.- Have fun.
7.- Be healthy.
8.- Take care of yourself and the ones you love.
9.- Never limit yourself.
10.- Always try new things and never give up.
-Why music influences people?
Why music influences people? Well, that is because a number of reasons and there are tons of different opinions about it. My opinion on why it influences us is because it is a huge part of our life, there will never be a single day we don´t listen to music.
Scientifically we know that the influence of music touches the senses from without.
Music is a way of life, it has existed forever and will always exist, music always helps to relax, it also motivates people and makes them happy.
In a social way it is a component of every one's life, it influences people's movement and behavior. Many people always carry around their portable music players almost everywhere and listen to their favorite music whenever it is possible. Sometimes music also influences people's appearance, the different kinds of music can divide people into categories as well.
The power that music has on a person is influenced by the grade of spiritual evolution and the mentality the person has.
In some cases music is enjoyed more by people with good ear or musical conditions, once you know music or play a musical instrument, you listen to it in a different way, more deeply and analytically, and also what is received goes deeper into the soul and to the feelings.
-Mun Paper:
1.- What are the six main bodies of the UN?
A: General Assembly, Security Council, Economic and Social Council, Trusteeship Council, International Court of Justice, Secretariat.
2.-Which countries are not members of the UN?
A: Kosovo, Taiwan, Vatican City/The Holy See .
3.- When did Japan join the UN?
A: On the 18th of December, 1956.
4.- Who's the present Secretary General of the UN?
A: Ban Ki-moon.
5.- When is united nations day?
A: 24th of October.
6.- What's the origin and purpose of the permanent five as they relate to the United Nations?
A: The five permanent members of the security council were the big five victorious powers in World War II. (USA, UK, France, China, and Russia.) You could view it as the spoils of war, or the winners' guarantee that the same war doesn't happen again.
It is also interesting to note that these power these countries have enable them to do as they like and simply veto any move that may stand in their way regardless of the objections of the majority of the other members of the UN.
The P5 themselves, and their academic supporters, argue that they hold the power of veto as they are responsible for enforcing Security Council resolutions and ensuring International Peace and Security itself. Thus, they should not be forced into supporting a situation they do not agree with and sacrificing their own soldiers. Though, this does create a situation where SC countries can shield their allies, like the US protecting Israel, or China defending North Korea, or Russia supporting Iran.
7.- Why didn´t the US join the league of the nations?
A: Despite all Woodrow Wilson's efforts in establishing the League of Nations, the USA did not join the League because of objections raised in the Senate, especially from Republican politicians William E Borah and mainly Henry Cabot Lodge, and Wilson's refusal to compromise ensured that the US would not ratify the Covenant of The League of Nations and the Treaty of Versailles.
Joining the League of Nations would be like signing a blank cheque - America didn't want to have to ship its troops half way across the world for disputes that didn't concern them. It didn't want to risk its economy or any more American lives after the losses of WW1. The Republicans wanted to return to Isolationism - being an independent country and not involving itself in other countries affairs.
America also strongly disagreed with the Treaty of Versailles. Many Germans lived in America and Americans felt it was far too harsh. One of the Leagues aims was to uphold the Treaty of Versailles which made some Americans very averse to joining the League.
8.- Who was the president when the US became part of the UN
A: Harry S. Truman.
9.- What nations are involved in the UN?
Afghanistan
Albania
10.- How many nations are involved in the UN?
A: 192 Nations.
11.- What's the purpose of the UN?
A: To provide a place for countries to do two things. First, allows countries a neutral means of communication. Second the United Nations is in a basic sense a world government.
12.- Which body of the UN is like a parliament of nations which meets to consider the world's most pressing problems?
A: The General Assembly.
13.- Where's the headquarters of the UN loaded?
A: New York City
14.- How was the UN involved in the Vietnam War?
A: They opposed the war effort.
The war was a multilateral invasion by the US, without UN Security Council support.
The United Nations was used as a spark point for protests - On the 9th of November, 1965, Catholif Worker Movement member Roger Allen LaPorte self-immolated in front of the UN HQ building in New York City.
In fairness to America, the situation in the Security Council would have meant that a UNSC Resolution would have been nearly impossible.
15.- What's the role of the UN in the decolonization of Angola?
A:
16.- What are the contributions to the world peace by the UN or any of it's agencies?
A:
17.- What's the role of the UN in the world's affairs?
A: T he UN helps bring together countries in an internationl forum to settle disputes and problems. The UN has programs like UNESCO and all these other programs to help feed poor people and provide some other forms of aid.
-Why music influences people?
Why music influences people? Well, that is because a number of reasons and there are tons of different opinions about it. My opinion on why it influences us is because it is a huge part of our life, there will never be a single day we don´t listen to music.
Scientifically we know that the influence of music touches the senses from without.
Music is a way of life, it has existed forever and will always exist, music always helps to relax, it also motivates people and makes them happy.
In a social way it is a component of every one's life, it influences people's movement and behavior. Many people always carry around their portable music players almost everywhere and listen to their favorite music whenever it is possible. Sometimes music also influences people's appearance, the different kinds of music can divide people into categories as well.
The power that music has on a person is influenced by the grade of spiritual evolution and the mentality the person has.
In some cases music is enjoyed more by people with good ear or musical conditions, once you know music or play a musical instrument, you listen to it in a different way, more deeply and analytically, and also what is received goes deeper into the soul and to the feelings.
-Mun Paper:
1.- What are the six main bodies of the UN?
A: General Assembly, Security Council, Economic and Social Council, Trusteeship Council, International Court of Justice, Secretariat.
2.-Which countries are not members of the UN?
A: Kosovo, Taiwan, Vatican City/The Holy See .
3.- When did Japan join the UN?
A: On the 18th of December, 1956.
4.- Who's the present Secretary General of the UN?
A: Ban Ki-moon.
5.- When is united nations day?
A: 24th of October.
6.- What's the origin and purpose of the permanent five as they relate to the United Nations?
A: The five permanent members of the security council were the big five victorious powers in World War II. (USA, UK, France, China, and Russia.) You could view it as the spoils of war, or the winners' guarantee that the same war doesn't happen again.
It is also interesting to note that these power these countries have enable them to do as they like and simply veto any move that may stand in their way regardless of the objections of the majority of the other members of the UN.
The P5 themselves, and their academic supporters, argue that they hold the power of veto as they are responsible for enforcing Security Council resolutions and ensuring International Peace and Security itself. Thus, they should not be forced into supporting a situation they do not agree with and sacrificing their own soldiers. Though, this does create a situation where SC countries can shield their allies, like the US protecting Israel, or China defending North Korea, or Russia supporting Iran.
7.- Why didn´t the US join the league of the nations?
A: Despite all Woodrow Wilson's efforts in establishing the League of Nations, the USA did not join the League because of objections raised in the Senate, especially from Republican politicians William E Borah and mainly Henry Cabot Lodge, and Wilson's refusal to compromise ensured that the US would not ratify the Covenant of The League of Nations and the Treaty of Versailles.
Joining the League of Nations would be like signing a blank cheque - America didn't want to have to ship its troops half way across the world for disputes that didn't concern them. It didn't want to risk its economy or any more American lives after the losses of WW1. The Republicans wanted to return to Isolationism - being an independent country and not involving itself in other countries affairs.
America also strongly disagreed with the Treaty of Versailles. Many Germans lived in America and Americans felt it was far too harsh. One of the Leagues aims was to uphold the Treaty of Versailles which made some Americans very averse to joining the League.
8.- Who was the president when the US became part of the UN
A: Harry S. Truman.
9.- What nations are involved in the UN?
Afghanistan
Albania
Algeria
Andorra
Angola
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
Brunei Darussalam
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cape Verde
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Colombia
Comoros
Congo
Costa Rica
Côte D'Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Denmark
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatoral Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Ethiopia
Fiji
Finland
France
Gabon
Gambia
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Greece
Grenada
Guatemala
Guinea
Guinea Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Japan
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Lao People’s Democratic Republic
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mexico
Micronesia
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Norway
Oman07
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Poland
Portugal
Qatar
Republic of Korea
Republic of Moldova
Romania
Russian Federation
Rwanda
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Suriname
Swaziland
Sweden
Switzerland
Syrian Arab Republic
TTajikistan
Thailand
The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Tuvalu
UUganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
United Republic of Tanzania
United States of America
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
VVanuatu
Venezuela
VietNam
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe.
10.- How many nations are involved in the UN?
A: 192 Nations.
11.- What's the purpose of the UN?
A: To provide a place for countries to do two things. First, allows countries a neutral means of communication. Second the United Nations is in a basic sense a world government.
12.- Which body of the UN is like a parliament of nations which meets to consider the world's most pressing problems?
A: The General Assembly.
13.- Where's the headquarters of the UN loaded?
A: New York City
14.- How was the UN involved in the Vietnam War?
A: They opposed the war effort.
The war was a multilateral invasion by the US, without UN Security Council support.
The United Nations was used as a spark point for protests - On the 9th of November, 1965, Catholif Worker Movement member Roger Allen LaPorte self-immolated in front of the UN HQ building in New York City.
In fairness to America, the situation in the Security Council would have meant that a UNSC Resolution would have been nearly impossible.
15.- What's the role of the UN in the decolonization of Angola?
A:
16.- What are the contributions to the world peace by the UN or any of it's agencies?
A:
17.- What's the role of the UN in the world's affairs?
A: T he UN helps bring together countries in an internationl forum to settle disputes and problems. The UN has programs like UNESCO and all these other programs to help feed poor people and provide some other forms of aid.
18.- Who was the Secretary General of UN during the 1960`s ?
A: U Thant.
19.- UN founders.
A: There were 51 founding members of the United Nations:
South Africa
Argentina
Australia
Belarus
Belgium
Bolivia
Brazil
Canada
Czechoslovakia
Chile
Republic of China
Colombia
Costa Rica
Cuba
Denmark
Egypt
El Salvador
Ecuador
Ethiopia
France
Greece
Guatemala
Haiti
Honduras
India
Iran
Iraq
Lebanon
Liberia
Luxembourg
Mexico
Nicaragua
Norway
New Zealand
Panama
Paraguay
Filipino Netherlands
Peru
Poland
Dominican Republic
the United Kingdom
Saudi Arabia
Syria
Turkey
Ukraine
Union of the Soviet Socialist Republics (the USSR)
The United States of America (USA)
Uruguay
Venezuela
Yugoslavia 20.- What did the UN do to help the Rwanda genocide?
A: Rwandan genocide occurred in 100 days in 1994. This was a fight for power involving the Tutsis and the Hutus ethnic groups. Hutus began to slaughter all Tutsis in the aim to demolish this entire ethnic group, an as a result, killing 800000 people.
1992 Ceasefire/ peace talks open
1993 UN began their peacekeeping mission
1994 President Habyarimana was killed near Kigali (Smith, D, 2003)
The world along with the UN failed to act and respond quick enough to stop these killings and end the genocide. 5500 UN troops were sent over to Rwanda, and international leaders were warned of the slaughters however no one believed or took any measures to prevent. (Murray, P, 2004)
"Rwanda's tragedy was the world's tragedy in their greatest hour of need; the world failed the people of Rwanda" General Kofi Annan.
21.- How did the UN help the earthquake in Kashmir?A: Eneficiaries, which covered emergency shelter, health, nutrition and water hygiene and sanitation; and Cross-Cutting Concerns, with three clusters: early recovery, protection and camp coordination and management. Other sectors which the UN considered had clear leadership and accountability, such as agriculture (led by FAO), refugees (UNHRC-led), education (UNICEF) and food (WFP), were not included in the cluster approach.
22.- Who was the first elected Secretary General of the UN?A: Gladwyn Jebb.
23.- What was the forerunner of the UN?A: President Franklin D. Roosevelt
24.- When was the UN born?A: 1945.
1993 UN began their peacekeeping mission
1994 President Habyarimana was killed near Kigali (Smith, D, 2003)
The world along with the UN failed to act and respond quick enough to stop these killings and end the genocide. 5500 UN troops were sent over to Rwanda, and international leaders were warned of the slaughters however no one believed or took any measures to prevent. (Murray, P, 2004)
"Rwanda's tragedy was the world's tragedy in their greatest hour of need; the world failed the people of Rwanda" General Kofi Annan.
21.- How did the UN help the earthquake in Kashmir?A: Eneficiaries, which covered emergency shelter, health, nutrition and water hygiene and sanitation; and Cross-Cutting Concerns, with three clusters: early recovery, protection and camp coordination and management. Other sectors which the UN considered had clear leadership and accountability, such as agriculture (led by FAO), refugees (UNHRC-led), education (UNICEF) and food (WFP), were not included in the cluster approach.
22.- Who was the first elected Secretary General of the UN?A: Gladwyn Jebb.
23.- What was the forerunner of the UN?A: President Franklin D. Roosevelt
24.- When was the UN born?A: 1945.
25.- What are the components of the General Assembly of the UN?
A:
26.- Why did the UN send an army to the south of Korea in 1950?
A: To answer North Korea's aggression, restore regional stability and return
the border between North and South Korea to the 38th parallel.
27.- What do Oliver branches on the UN flag represents?
27.- What do Oliver branches on the UN flag represents?
A: The olive branches are a symbol for peace, and the world map represents all the people of the world.
28.- When did new Zeeland join the UN?
A: 24 October 1945.
29.- Why didn’t the UN get involved during the cold war?
A:
30.- Who is the best popular UN member?
A:
This week was really good, and I felt more integrated with the subject, I think it was awesome that we got to write about the influence of music in people because I really enjoy music.
My goals are to get better and make a good oral presentation next week.
This week was really good, and I felt more integrated with the subject, I think it was awesome that we got to write about the influence of music in people because I really enjoy music.
My goals are to get better and make a good oral presentation next week.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
















